What is 3D Printing?
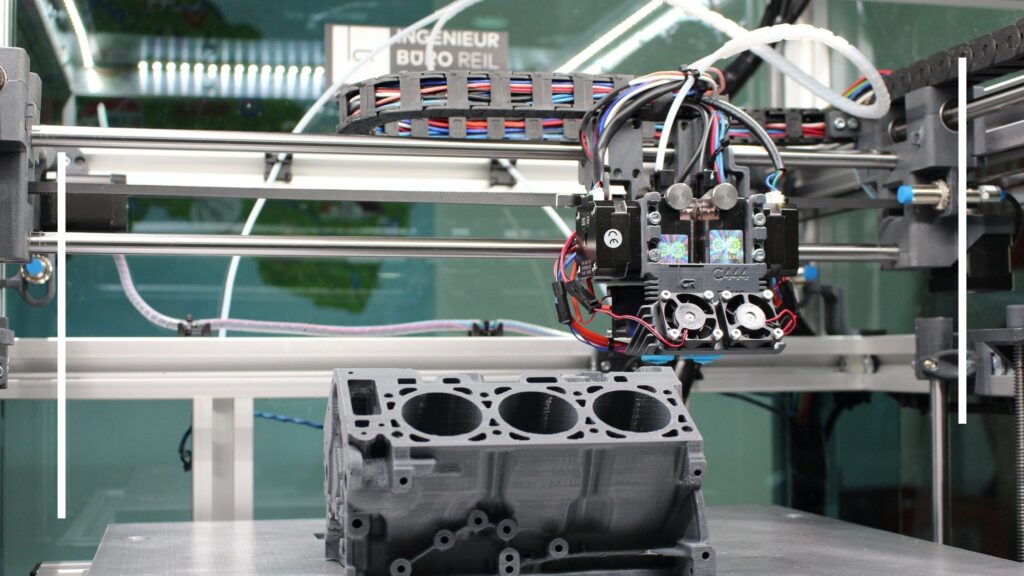
Imagine being able to create almost anything you can dream up, layer by layer, right from a computer file. That’s the magic of 3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing. Unlike traditional methods that often involve cutting or shaping material from a larger piece, 3D printing builds objects from scratch, one layer at a time. It’s like sculpting in reverse—starting with nothing and adding material to make something incredible.
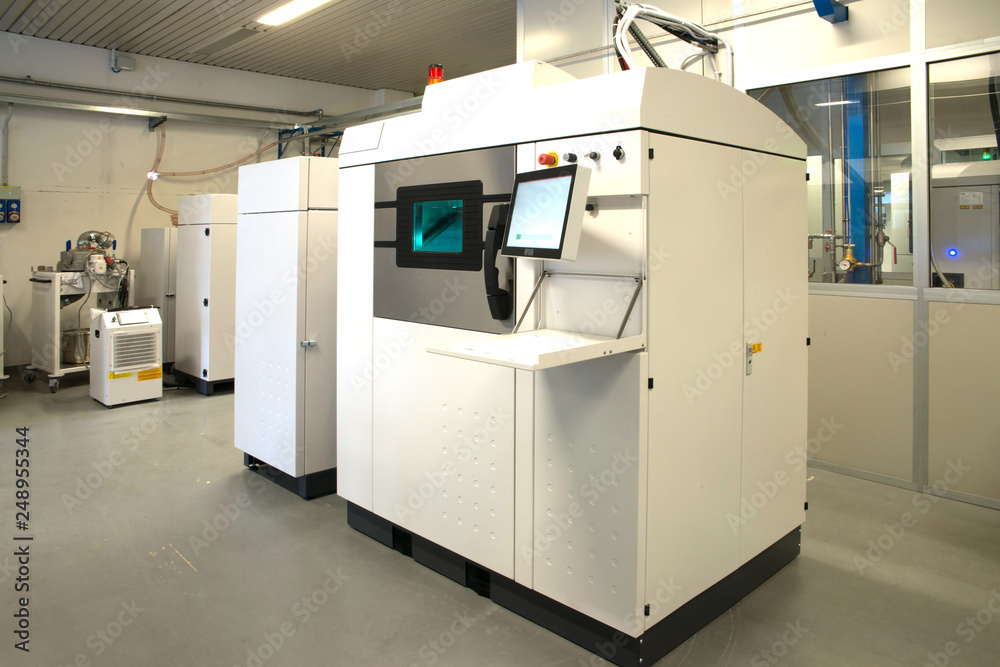
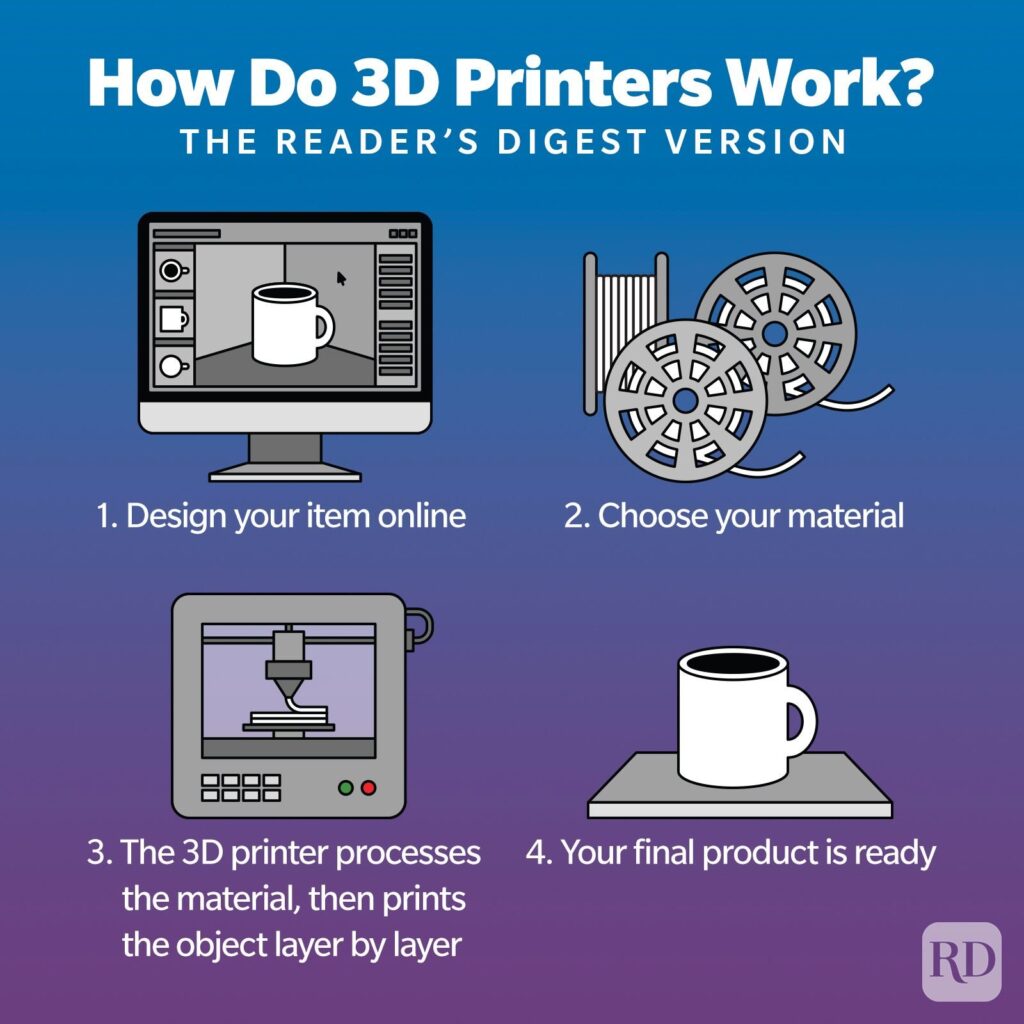
1: How Does 3D Printing Work?
Design: It all begins with a digital 3D model. You can design this yourself using computer-aided design (CAD) software, or you might use a 3D scanner to capture an existing object. This model is then sliced into thin layers by special software, turning it into a format the 3D printer can understand.
Printing: The sliced model is sent to the 3D printer, which starts building the object layer by layer. Depending on the printer, it could use materials like plastic filament, resin, or even metal powder. Each layer sticks to the one below it, slowly creating the final object.
Post-Processing: Once printing is complete, the object might need some extra work. This can include removing support structures, smoothing out surfaces, or adding finishing touches like paint. This step ensures the final product looks just right and works as intended.
2: Types of 3D Printers
There are different types of 3D printers out there, each with its own strengths: Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM): FDM printers are like the everyday workhorses of 3D printing. They use plastic filaments that are melted and extruded to build up the object layer by layer. They’re affordable and easy to use, making them a favorite for hobbyists and those new to 3D printing.
1: Stereolithography (SLA): SLA printers use ultraviolet light to cure liquid resin into solid layers. They’re known for their high precision and smooth finishes, which makes them perfect for detailed and intricate designs, like those used in jewelry or dental work.
2: Selective Laser Sintering (SLS): SLS printers use lasers to fuse powdered materials into solid objects. They’re great for creating strong, functional parts with complex shapes, making them popular in industries like aerospace and automotive.
3: Digital Light Processing (DLP): DLP printers are similar to SLA but use a digital light projector to cure resin. They offer faster printing speeds and high detail, which is ideal for projects requiring fine accuracy.
4: Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS): DMLS is a type of SLS that focuses on metal printing. It’s used to create high-strength metal parts for fields like aerospace and medical implants, where durability and precision are crucial.
3: Applications of 3D Printing:
3D printing is incredibly versatile and is making waves in various fields:
1: Prototyping: Rapid prototyping is one of the coolest uses of 3D printing. Designers and engineers can quickly turn their ideas into physical models, speeding up the process of development and saving money compared to traditional methods.
2: Manufacturing: Imagine being able to produce custom parts on demand without needing to keep a huge inventory. 3D printing makes this possible, cutting down on waste and allowing for the creation of complex designs that traditional methods can’t handle.
3: Healthcare: In the medical world, 3D printing is nothing short of revolutionary. It’s used to make personalized prosthetics, custom implants, and even 3D-printed tissues. This means treatments can be tailored to individual patients, improving outcomes and care.
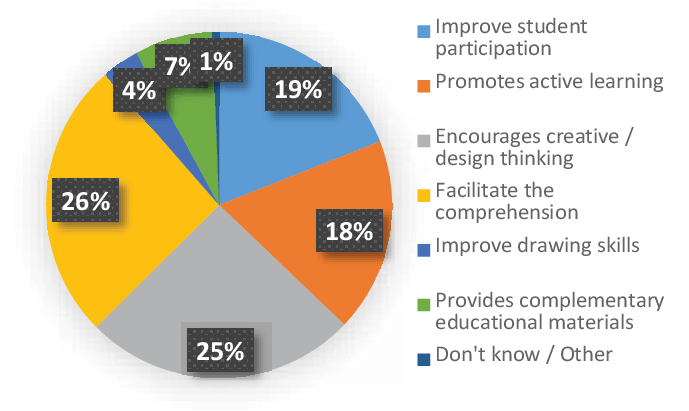
4: Education: 3D printers in classrooms offer a hands-on way for students to learn. They can create their own designs, explore engineering concepts, and see their ideas come to life. It’s a fantastic tool for making complex theories more accessible and engaging.
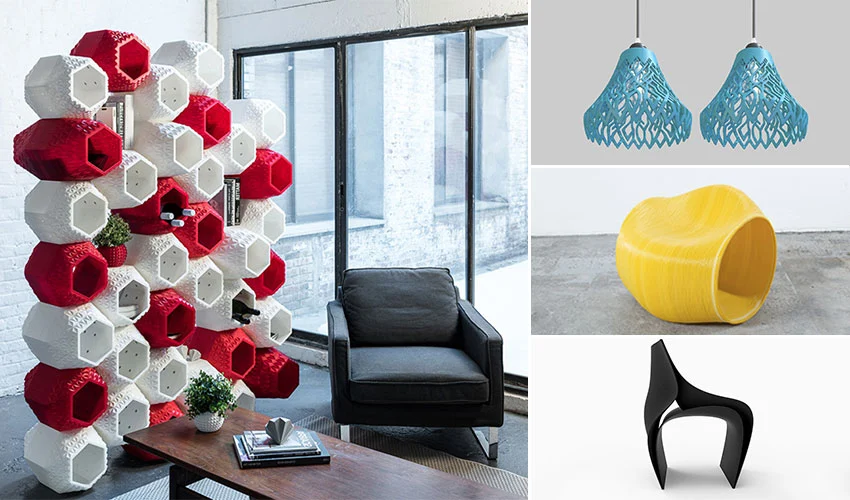
5: Art and Design: Artists and designers are using 3D printing to push creative boundaries. From detailed sculptures to custom jewelry, 3D printing opens up new possibilities for artistic expression and innovation.



What is 3D Printing? Imagine being able to create almost anything you can dream up, layer by layer, right from.. Read more
The Future of Manufacturing: Exploring the World of 3D Printing




3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a process of creating three-dimensional objects from a digital file by layering materials until the object is formed.
3D printing works by slicing a digital model into thin layers, which are then printed layer by layer to create the final object. The printer follows the digital file’s instructions to deposit material where needed.
The cost of 3D printing varies based on the material, complexity of the design, and the type of 3D printer used. While the initial investment can be high, it can save money in the long run by reducing waste and prototyping costs.